Chap.11 计算小白硬学VASP —— 构建slab模型
¡Hola a todos!
本章介绍如何构建slab模型。
首先切面用到的miller index针对的是bulk模型的惯用胞(conventional cell)而不是原胞(primtive cell),这与之前计算能带是刚好相反的。
所以,在进行切面操作时,要确保你的bulk模型是惯用胞,可以用pymatgen的功能来帮助实现。
- 直接从
Materials project下载结构
如果是从MP上下载结构,我们需要把conventional_cell = True打开:
1 | from mp_api.client import MPRester |
这样确保你下载的结构是惯用胞。
- 原胞转化为惯用胞
也可以通过转化来确保使用的是惯用胞:
1 | from pymatgen.core.structure import Structure |
new_structure对应的就是惯用胞结构。运行代码:
1 | old structure: |
或者你不知道自己的结构到底是原胞还是惯用胞,可以无脑直接转换,因为对于本身就是惯用胞的结构,get_conventional_standard_structure()方法不会修改本身的信息:
1 | from pymatgen.core.structure import Structure |
结果不变,运行代码:
1 | old structure: |
Note:上述方法对于缺陷结构和掺杂结构,由于对称性无法识别可能无法转化。
SlabGenerator模块
进入正题,切面主要用到pyamtgen的SlabGenerator模块,首先导入它:
1 | from pymatgen.core.surface import SlabGenerator |
然后需要先实例化SlabGenetator,才能调用里面的切面方法:
1 | from pymatgen.core.surface import SlabGenerator |
这里着重介绍in_unit_planes和primitive参数。
in_unit_planes:影响min_slab_size和min_vacuum_size的数值,默认为False。当为
False时,min_slab_size和min_vacuum_size对应的单位为Angstrom,即上述分别表示slab厚度为10埃,真空层厚度为15埃;当为
True时,数值为切面的层数,如此时min_slab_size和min_vacuum_size都设置为3,表示slab厚度和真空层厚度为(1,1,1)面最小重复单元乘以3。需要注意的是,此时数字3并不等于原子层数,且不同晶面的最小重复单元的厚度不一样,如Si的(1,1,1)面单层厚度是小于(1,0,0)面的。
primitive:默认为True。该参数跟primitive cell没有关系,在这里是决定slab结构是否选取最小单元。当设置为True时,如1x1x1的Si惯用胞结构和3x3x3超胞的Si惯用胞结构,最后得到的slab结构是一样。
SlabGenerator下面有许多切面的方法,下面一一介绍。
get_slab()方法
get_slab()方法用于生成指定暴露面原子的slab结构,传入shift参数来指定原子。该方法不建议直接使用,前提你需要确定shift的值。对于垂直于坐标轴的切面,shift值对应的分别就是abc的坐标,但是其他晶面情况就需要简单的运算之后才能够得到shift值。代码如下:
1 | from pymatgen.core.surface import SlabGenerator |
vesta里面查看结构:
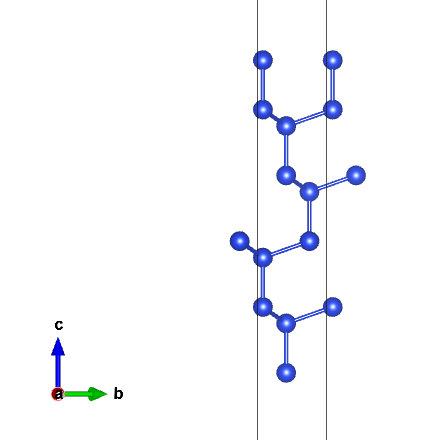
slab厚度和真空层厚度可根据上述方法自行调整。
get_slabs()方法
get_slabs()支持生成所有符合要求的slab,接受传入的参数也要比gen_slab()多,主要有:
bonds:设置成键范围。通俗的讲就是保护指定原子键对,避免断键。如LiFePO4中要保护PO4基团不被切断键,可以设置bonds={(“P”, “O”): 3},这样就告诉pymatgen,3埃范围内的P原子和O原子维持成键,切面时就会避开PO4断键了。max_broken_bonds:自动切表面时,最大断键数,默认为0。建议不要主动设置,对于复杂结构,会导致切出的slabs数量急增。repair:自动补齐暴露面断键原子,默认False。也建议不要设置,会生成许多不可理的结构。
1 | from pymatgen.core.surface import SlabGenerator |
运行代码:
1 | [Structure Summary |
get_slabs()自动切出所有的表面,根据输出信息可以发现根据原子排布不同Si(1,1,1)面有两种暴露面:
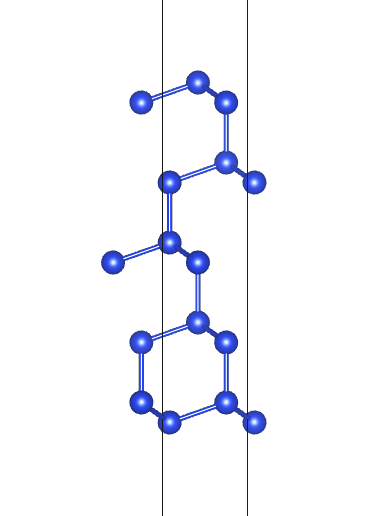
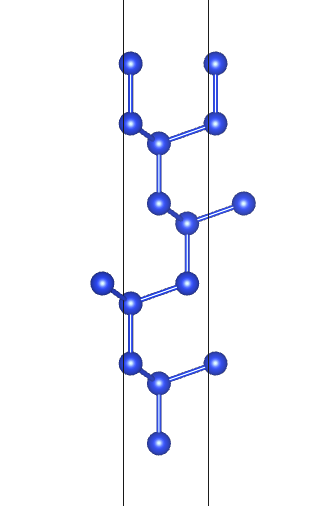
补充
pymatgen切面有时候slabc方向不是正交的,即γ角不为90°。此时可以调用get_orthogonal_c_slab()方法进行矫正即可,用法为直接在slab对象调用即可:
1 | ...... |
¡Muchas gracias!